Qt Designer Signals And Slots Tutorial
- Qt Creator Signals And Slots Tutorial
- Qt Designer Signals And Slots Tutorial Download
- Qt Designer Signals And Slots Tutorials
- Qt Designer Signals And Slots Tutorial Free
QGIS Tutorials
Qt 5 signals and slots mechanism. How signals and slots in Qt differ from the callback architecture in other widget toolkits. A Qt basics tutorial. How to add signals and slots in Qt Creator. Part 9 of the Qt Creator C Tutorial. Go to the Qt Programming Tutorial Series Table of Contents. A short roundup of Qt Designer, which ships with QGIS and is the recommended program to design Graphical User Interfaces for QGIS Plugins. This post is complementary to our plugin tutorials or just a refresher. It also explains resources.qrc files in more detail, a usual pain point. The signal and slot operation are used to handle events and signals of the objects or widgets at the python app development level. It will also enable communication between some designed objects. The following steps are needed for creating a Python signal and slot operations. Step 1 - Create QDialog (new form).
This tutorial is part of our QGIS tutorial series:

Qt Designer is an easy-to-use program to build UI's for Qt frameworks. Luckily, QGIS ships the program with its core on all operating systems and should be available as an executable on your computer.
It's the easiest way to create and alter UI files for QGIS plugins.
Basic vocabulary
Qt Creator Signals And Slots Tutorial
UImeansuser interfaceOSmeansoperating systemGUImeansgraphical user interface
Short roundup of Qt Designer

In the startup dialog, create a new Dialog with Buttons Bottom dialog, which will give you a bare-bone UI. For easier navigation, here's a quick breakdown of the Qt Designer interface:
1 Available widgets
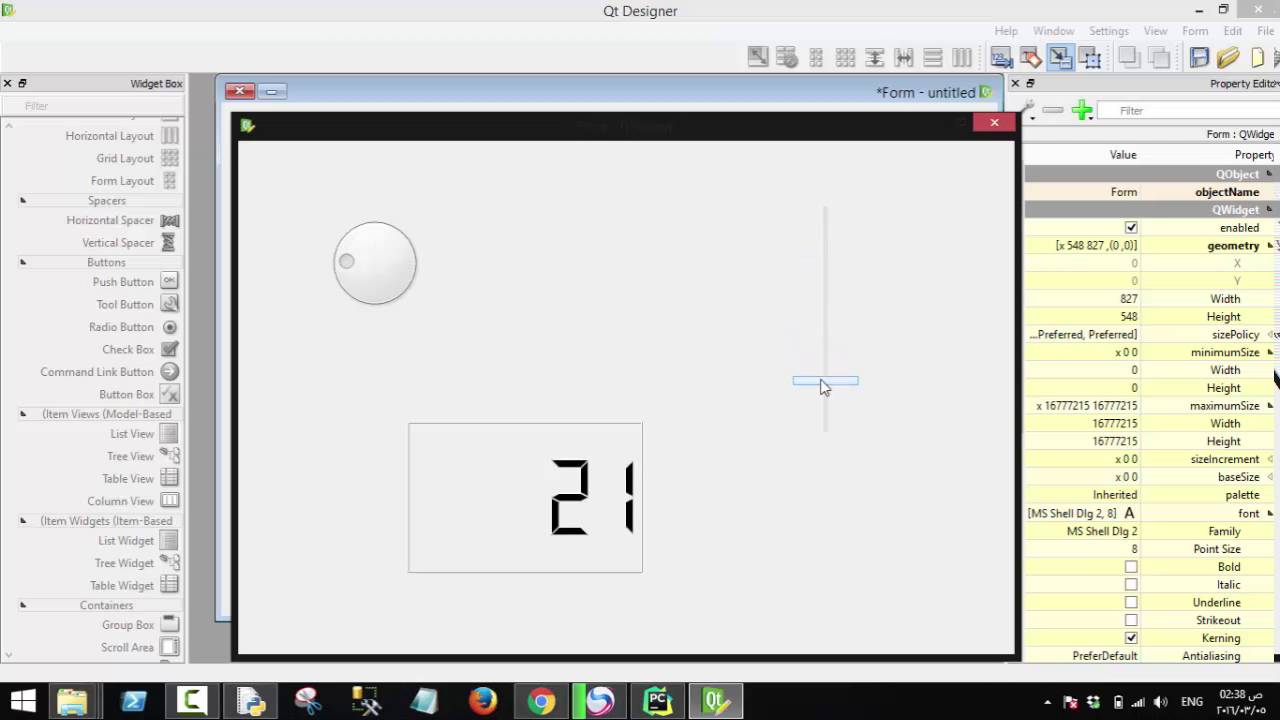
In Qt, all GUI elements are classified as Widgets, which can have all kinds of actual UI functionality like buttons, containers or user input elements. Drag a few widgets into your dialog and experiment a bit. There's also several custom QGIS widgets at the very bottom, which extend functionality of Qt widgets (like CRS picker).
2 Object inspector
You can click on widgets in your dialog to select them. But sometimes it's good to see the hierarchy of widgets or select it from a list, e.g. when they are overlapping each other in the dialog.
3 Property Editor
Each widget exposes a list of properties, like geometry or font, which you will find in this panel. You didn't see any actual code yet, but these properties are accessible methods through the Python class of your GUI. So it's also a good reference to available widget properties to be modified. It gives you a whole lot more information though:
- the name you give the widget
- the PyQt5 class name, e.g.
QDialogButtonBoxfor the OK/Cancel button group - you can immediately see the sub-classing for each widget by examining the tabs of the Property dialog. E.g. the
QDialogButtonBoxis sub-classed from (in descending order):QObject, which only exposes theobjectNameproperty and will be widget identifier in your codeQWidget, which exposes multiple properties, mostly layout related- and finally
QDialogButtonBox, which has mostly functional properties, e.g. which buttons are displayed
4 Layout toolbar
Quick access to different layouts for container widgets, see its importance right below.
Important Qt Designer concepts
Every container widget needs a layout!. Layouts help in... well, layouting (to keep consistent element spacing when resizing etc.). Try out different layout types and add a few widgets to see the behavior.
Every widget needs a unique name property defined in
QObject.objectName! It will auto-name your widgets and while it's not required it's highly recommended to use structured naming for widgets. It will help a lot when you access them in the code later on, which becomes more important with a multitude of widgets.Size policies are important! When building bigger GUIs it will be increasingly important to define how widgets behave visually within their layout. When the user changes the window size, it can be disorienting if a button scales with the resizing. Size policies define the widget's size behavior within the layout.
Qt resources.qrc
Qt has the concept of an in-app resource store, which is defined in resources.qrc files on a plugin level. That file has a XML structure and is used to register binary files, like PNG images, with Qt in-app. Making use of this internal resource store is of advantage to:
- use images directly in Qt Designer
- omit path builders in Python to locate those files
The resources.qrc file has to be compiled to a Python file, e.g. resources.py by running pyrcc5 -o resources.py resources.qrc. The compilation will encode all binary files found in resources.qrc and include them as binary strings in resources.py. When you import the Python file in the main Python module of a QGIS plugin, all specified files will be registered in QGIS and accessible in your Python code via their shorthand URI ':<prefix>/<file_path>'.
Structure
The basic structure is:
Qt Designer Signals And Slots Tutorial Download
A qresource is like a directory for files. It has a prefix to distinguish plugin resources from each other and QGIS core resources.
One or more file descriptors can be registered per qresource. The path specified here is relative to the resouces.qrc file. If the image was located in ./gui/image/, the path would be gui/image/icon.png.
Alternatively you can add more files via Qt Designer (View ► Resource Browser).
Using resources.qrc
In Python

When you compiled the resource file to resources.py, just import the module in the main module of your plugin, e.g. from resources import *. That will magically register all resources with QGIS and your plugin, even though no objects are directly called.
Then you can access the registered files with ':<prefix>/<file_path>', e.g. icon_path = ':/plugins/quick_api/icon.png'. That works plugin-wide, without re-importing resources anywhere else.
Qt Designer Signals And Slots Tutorials
In Qt Designer
Qt Designer Signals And Slots Tutorial Free
If you load the resource file in View ► Resource Browser, you can use the registered files in the same way as in Python. E.g. when you set the HTML on a QLabel and need to insert an image, you can do